In the enthralling world of paleontology, every fossil find has the potential to unveil new chapters in the history of life on Earth.

The Dilong, a remarkable dinosaur with a pivotal role in early avian evolution, is one such groundbreaking discovery. This article takes you on a journey into the world of the Dilong, its fossil significance, and the profound insights it provides into the origins of avian creatures.
The Dilong, which translates to “emperor dragon,” lived during the Early Cretaceous period, approximately 130 million years ago. It was a small theropod dinosaur, measuring about six feet in length. While its size may not have been imposing, its significance in the world of paleontology is monumental.

What sets the Dilong apart from other dinosaurs is the presence of well-preserved feathers in some of its fossils. The existence of feathers in a theropod dinosaur offers compelling evidence of the evolutionary link between dinosaurs and birds. This connection revolutionized our understanding of avian evolution.
The presence of feathers in the Dilong has profound implications for our understanding of early avian evolution. It suggests that feathers, initially evolved for insulation or display purposes, eventually led to the development of flight in avian creatures. This evolutionary shift from feathered dinosaurs to true birds marked a pivotal moment in Earth’s biological history.
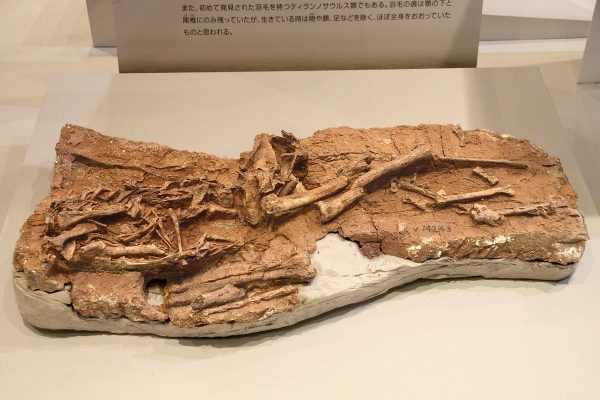

The Dilong is part of a broader group of theropod dinosaurs, some of which eventually gave rise to the first true birds. This transition from terrestrial dinosaurs to flying avian creatures represented one of the most extraordinary adaptations in the history of life on Earth.
Feathers played a central role in this transition, providing not only insulation but also aiding in mobility and eventually enabling powered flight. The Dilong’s fossils and the feathers they preserved offer a window into this transformative journey.
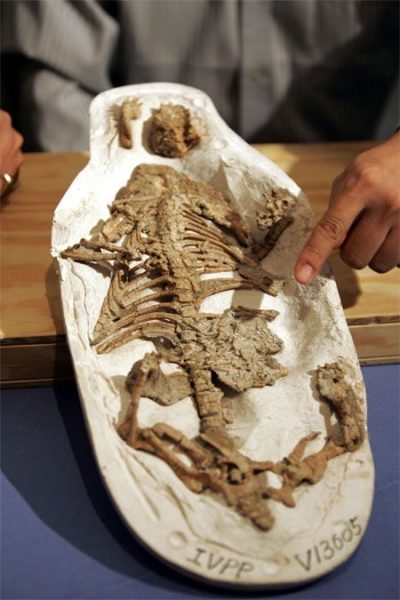
The discovery of the Dilong and its feathers has diverse implications for paleontology, evolutionary biology, and our understanding of Earth’s history. It highlights the complex interplay between environmental changes, adaptation, and speciation. The evolution of feathers, originally for purposes other than flight, showcases nature’s propensity for repurposing structures for novel functions.
In the grand narrative of life on our planet, the Dilong stands as a symbol of the interconnectedness of Earth’s biological history. Its fossils, with their well-preserved feathers, provide a unique and invaluable glimpse into the evolution of avian creatures.

The Dilong is a reminder that paleontology continues to illuminate the deep history of our planet. Its significance in the context of early avian evolution underscores the ongoing nature of scientific discovery, as each fossil find enriches our understanding of Earth’s past.





