The Triassic period, which spanned from approximately 252 to 201 million years ago, marked a crucial juncture in the Earth’s history. During this time, the planet underwent significant changes, including the diversification of life forms and the emergence of iconic prehistoric creatures.

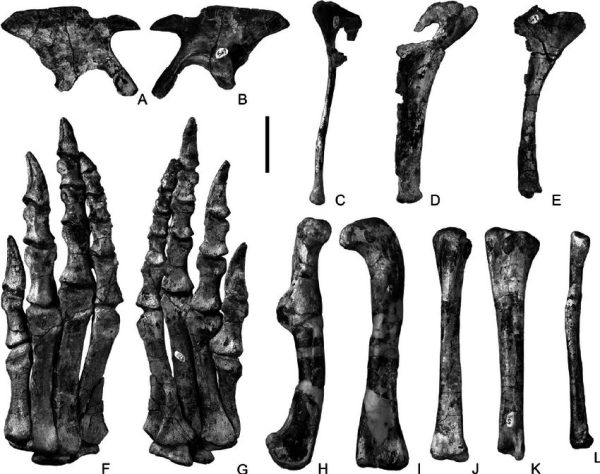
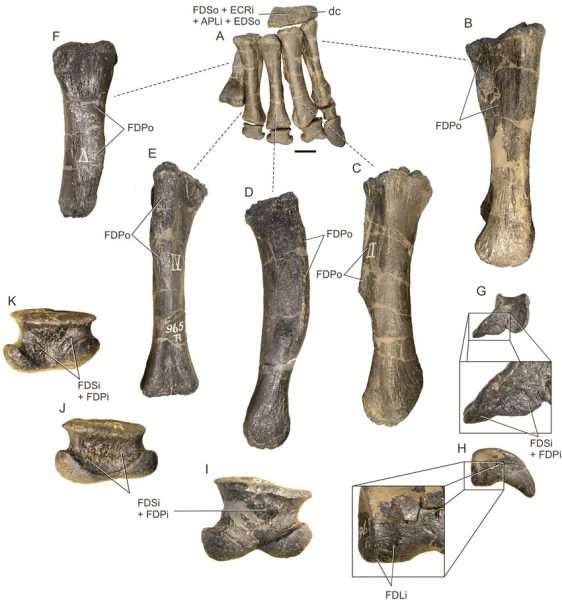
Recently, an exciting paleontological discovery in South America has unveiled a Triassic treasure – Adeopapposaurus fossils – shedding light on life 215 million years ago.
Adeopapposaurus is a remarkable find in the world of paleontology, as it belongs to the group of early dinosaurs known as “sauropodomorphs.” These long-necked and herbivorous dinosaurs ultimately gave rise to the enormous sauropods, including famous giants like Brachiosaurus and Diplodocus.
The discovery of Adeopapposaurus fossils in South America is particularly significant because it provides critical insights into the evolutionary history of these iconic long-necked dinosaurs.

Adeopapposaurus existed approximately 215 million years ago, making it one of the earliest sauropodomorph dinosaurs known to date. Studying its fossilized remains can help researchers understand the morphological and behavioral adaptations that paved the way for the later, massive sauropods.
The fossils offer a glimpse into the size, shape, and lifestyle of Adeopapposaurus. By examining the skeletal structure and other preserved features, paleontologists can estimate its size, posture, and potential feeding habits.
This information contributes to our broader understanding of how these early sauropodomorphs navigated their environments and interacted with other organisms.
Moreover, the geographical location of the discovery is noteworthy. South America played a crucial role in the history of Earth’s landmasses, serving as a land bridge between the ancient supercontinent of Pangaea and the southern continents.
Fossil findings in this region provide valuable data about the movement and distribution of life during the Triassic period, offering a glimpse into the geological history of the continent.
Adeopapposaurus’s existence in South America adds to the growing body of evidence supporting the idea that the southern continents were key players in the evolution of dinosaurs during the Triassic.
As paleontologists continue to unearth more fossils in this region, a more comprehensive picture of prehistoric life in South America and its global implications emerges.
The study of Adeopapposaurus fossils represents a window into the past, revealing the intricate web of life that thrived over 200 million years ago. These discoveries are a testament to the dedication and expertise of paleontologists who tirelessly search for and meticulously analyze these prehistoric treasures.
Each fossil find takes us one step closer to unraveling the mysteries of Earth’s ancient inhabitants and the world they inhabited during the Triassic period.





