Deep within the icy expanse of Siberian permafrost, a stunning revelation has captivated the scientific community: the discovery of a perfectly preserved 3,500-year-old bear.
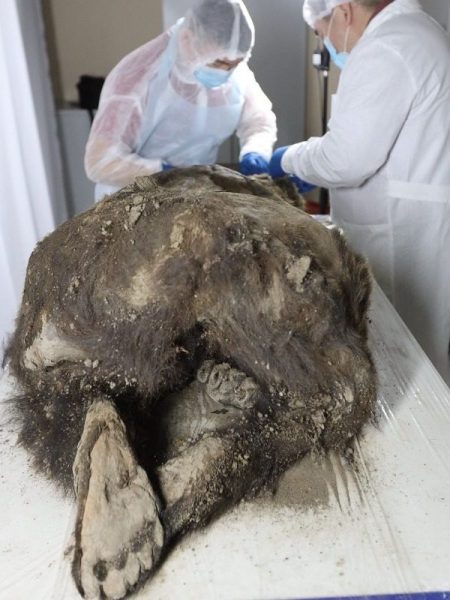
This find, nestled in the remote corners of Siberia, serves as a remarkable gateway to the past, unraveling mysteries of the Pleistocene epoch and shedding light on the enigmatic world that predates our own.
The bear, impeccably preserved by the permafrost’s unyielding grasp, presents scientists with an unprecedented opportunity to journey into history. Its fur, teeth, and internal organs, remarkably intact, transform this ancient creature into a treasure trove for researchers spanning paleontology, biology, and climatology.
A crucial focus for scientists is unraveling the mystery of the bear’s species. Through meticulous DNA analysis, researchers aim to clarify its taxonomic classification and understand its connection to modern bear species.
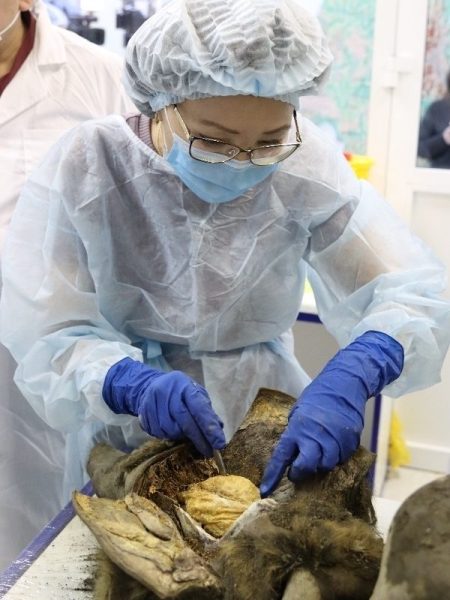

This investigation promises insights into the evolutionary trajectory of bears and their adaptations to changing environments over millennia.
The bear’s diet, revealed through the analysis of its stomach contents, offers a unique window into the ancient ecology of the region. Understanding the plant and animal species consumed by the bear allows scientists to reconstruct the available food resources during that era and gauge the potential impacts of environmental shifts.
Beyond its biological significance, this discovery contributes substantially to our understanding of climate change. Acting as a natural time capsule, the well-preserved specimen provides insights into the environmental conditions of Pleistocene Siberia.
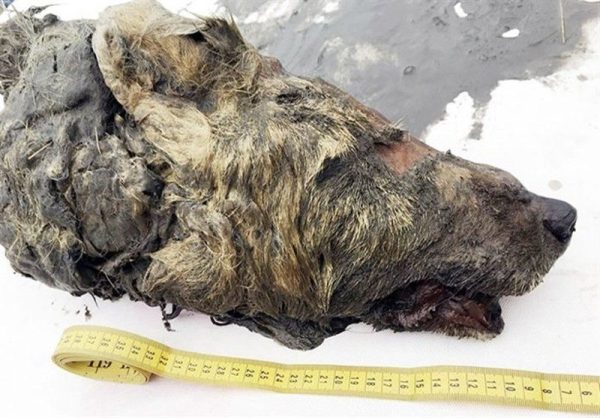

Studying the bear’s remains allows researchers to extract data on temperature, vegetation, and atmospheric conditions, refining climate models and enriching our understanding of Earth’s historical fluctuations.
Moreover, the discovery underscores the vulnerability of the Arctic permafrost, a critical concern amid contemporary climate change. As global temperatures rise, the thawing permafrost releases ancient organisms and carbon stores, introducing potential consequences for ecosystems and greenhouse gas emissions.

In essence, the exploration of this 3,500-year-old bear emerging from Siberian permafrost transcends a mere archaeological and paleontological pursuit.
It embarks on a multidisciplinary investigation, promising to deepen our understanding of prehistoric life, climate dynamics, and the challenges posed by ongoing environmental transformations.
This extraordinary find serves as a testament to the significance of preserving and studying our planet’s past, offering valuable insights to navigate the complexities of the future.





