New findings shed light on the cognitive capabilities of Thescelosaurus neglectus, a petite herbivorous dinosaur that roamed North America just before the cataclysmic end-Cretaceous extinction event 66 million years ago. Recent research by paleontologists David Button and Lindsay Zanno unveils intriguing aspects of this dinosaur’s sensory profile, hinting at its lifestyle and behavior.

Through the use of cutting-edge CT scanning technology, Button and Zanno delved into the preserved soft tissues of Thescelosaurus neglectus, reconstructing its brain and inner ear, which are typically lost in the fossilization process. These analyses revealed that this dinosaur possessed a relatively diminutive brain compared to its neornithischian counterparts, suggesting cognitive abilities akin to present-day reptiles.

Interestingly, Thescelosaurus neglectus exhibited a narrow hearing range, rendering it less adept at detecting high frequencies. Its auditory capabilities, while limited compared to some mammals, were finely attuned to low-frequency sounds, potentially aiding in detecting ground vibrations or the presence of predatory threats like the formidable T. rex.

Furthermore, the researchers noted an exceptional olfactory prowess in Thescelosaurus neglectus, with well-developed olfactory bulbs akin to those of modern-day alligators. This heightened sense of smell likely played a crucial role in foraging for buried plant matter such as roots and tubers, underscoring the dinosaur’s dietary habits and ecological niche.

Beyond olfaction, Thescelosaurus neglectus also showcased a remarkable sense of balance, crucial for navigating its environment with precision. This trait, coupled with its robust limbs and strong physical build, hints at potential digging or burrowing behaviors in its lifestyle, akin to modern subterranean animals.
The amalgamation of these sensory capabilities and physical attributes paints a vivid picture of Thescelosaurus neglectus as a highly specialized creature adapted to its ecosystem. While the exact extent of its subterranean activities remains speculative, the evidence strongly suggests a lifestyle intertwined with underground behaviors, mirroring ancestral adaptations of its lineage.
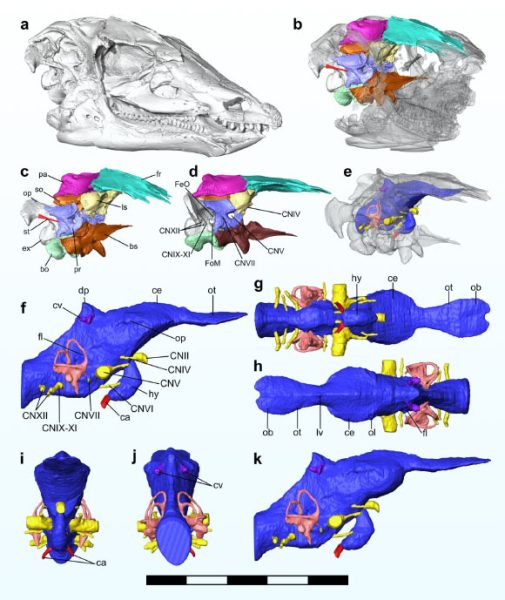
In essence, the seemingly unassuming Thescelosaurus neglectus unveils a fascinating tapestry of sensory adaptations and behaviors, offering a glimpse into the diverse evolutionary strategies employed by ancient organisms to thrive in their environments.
This research not only deepens our understanding of this enigmatic dinosaur but also underscores the intricacies of prehistoric life and the remarkable diversity of ancient fauna that once graced our planet.





